Cam 18 Test 2 – IELTS Writing Task 1
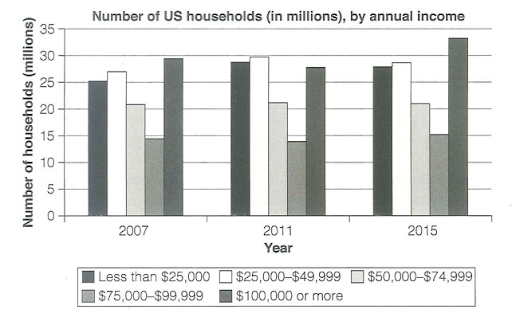
The bar chart compares the number of households categorized by annual income in the United States in three different years: 2007, 2011, and 2015.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
The bar chart presents data regarding the distribution of households in the United States based on their annual income from 2007 to 2015.
Overall, this period exhibits trivial changes in each annual income level. In 2007 and 2015, the most substantial proportions of households were those earning $100,000 and above annually; however, in 2011, a shift occurred as the peak moved to the $25,000 to $49,999 income bracket.
In 2007 and 2015, around 30 million households earned $100,000 or more each year, but it was slightly lower in 2011with about 27 million households falling into this category. Conversely, the $75,000-$99,999 income bracket consistently maintained the lowest figures, with approximately 15 million households belonging to this range during the three years. Despite its higher level, the $50,000-$74,999 income category demonstrated minimal variation throughout the depicted period, with just over 20 million households consistently falling within its boundaries.
The two lowest income groups, comprising households earning less than $25,000 and $25,000-$49,999, initially encompassed significant numbers, around 25 and roughly 27 million respectively. Subsequently, in 2011, both categories experienced marginal increases before slightly decreasing to approximately 28 and 29 million households respectively.
Từ vựng hay
1, Distribution (noun):
- The way something is shared out or arranged over a particular area or group.
- Example: The distribution of wealth in the country is highly unequal, with a small percentage of the population holding the majority of the resources.
2, Trivial (adjective):
- Of little value or significance; insignificant.
- Example: The changes observed in the data are quite trivial and do not significantly impact the overall trend.
3, Substantial (adjective):
- Large in amount, size, or importance.
- Example: There was a substantial increase in the number of students applying for scholarships this year.
4, Peak (noun):
- The highest point or level of something.
- Example: The peak of the mountain was covered in snow throughout the year.
5, Notably (adverb):
- Used to emphasize a particularly important fact or point.
- Example: Notably, the number of participants in the event increased significantly compared to last year.
6, Shift (noun):
- A change in position, direction, or focus.
- Example: There was a noticeable shift in consumer preferences towards organic products.
7, Consistently (adverb):
- In a regular and steady manner; without variation.
- Example: The company has consistently maintained high levels of customer satisfaction over the years.
8, Encompass (verb):
- To include a wide range of things.
- Example: The conference will encompass various topics related to sustainable development.
9, Boundary (noun):
- A limit or dividing line.
- Example: The river serves as a natural boundary between the two countries.
10, Marginal (adjective):
- Very small in amount or effect.
- Example: The increase in prices had only a marginal impact on consumer spending.
11, Initially (adverb):
- At the beginning; at first.
- Example: Initially, he found the new job challenging, but he eventually adapted to the role.
12, Subsequently (adverb):
- After a particular event or time; later.
- Example: The company faced financial difficulties and subsequently had to lay off some employees.
Bạn đang chuẩn bị cho kì thi IELTS?
Học IELTS Online qua ZOOM, bức band thần tốc
IELTS Thanh Loan – giáo viên 10 năm kinh nghiệm – trực tiếp đứng lớp, tự tin mang đến khóa học chất lượng nhất, phương pháp giảng dạy cô đọng dễ hiểu, giáo trình tự biên soạn cho lộ trình từ cơ bản đến luyện đề chuyên sâu. Đặc biệt, học viên luôn được quan tâm sát sao nhất, hỗ trợ không giới hạn, thúc đẩy kỷ luật học tập tốt để đạt mục tiêu.

Cam 18 Test 2 – IELTS Writing Task 2
Some university students want to learn about other subjects in addition to their main subjects. Others believe it is more important to give all their time and attention to studying for a qualification. Discuss both these views and give your own opinion.
While some argue that acquiring a broader knowledge base is essential for university students, others emphasize the significance of single-minded focus on specialization at tertiary level. This essay will delve into both perspectives before presenting my own viewpoint
Some university students advocate for a diverse range of subjects in addition to their core studies, arguing that a broader knowledge base can enhance their understanding of the world and foster critical thinking. For instance, a business major who also studies environmental science can better grasp the implications of corporate decisions on the environment, leading to more responsible and sustainable practices. This multidisciplinary approach enriches students’ learning experiences and equips them with a holistic view of societal issues.
On the contrary, there are those who contend that concentrating exclusively on their major is paramount, asserting that specialized knowledge and skills are essential in today’s competitive job market. Engineering students, for instance, may believe that dedicating their time solely to mastering intricate engineering concepts and techniques will give them an edge in the industry. This viewpoint suggests that intensive focus on one subject area can lead to expertise and a higher likelihood of success in a specific career path.
In my opinion, a balanced approach is advisable. While diversifying one’s academic pursuits can cultivate a well-rounded individual, undivided attention to a major can foster a deeper understanding and mastery of a particular field. This approach requires students to carefully manage their time and prioritize their studies, ensuring that they reap the benefits of both breadth and depth in their education.
To conclude, the question of whether to explore various subjects alongside the main major or to concentrate solely on it is multifaceted. A blend of both approaches, appreciating the advantages of each, offers students a comprehensive education that not only prepares them for the workforce but also enriches their intellectual growth.
Từ vựng hay:
1, Acquire a broader knowledge base:
- Getting a more extensive range of knowledge.
- Example: University education should focus on acquiring a broader knowledge base to prepare students for a diverse range of challenges in their future careers.
2, Single-minded focus on specialization:
- Concentrating solely on a specific area of study.
- Example: Some students believe that a single-minded focus on specialization is necessary to excel in their chosen field.
3, Delve into:
- Examine closely or thoroughly.
- Example: This essay will delve into both perspectives on the importance of a well-rounded education.
4, Core studies:
- Main subjects or primary areas of study.
- Example: Alongside their core studies, students should also explore other subjects that complement their academic journey.
5, Enhance their understanding:
- Improve or strengthen their comprehension.
- Example: Engaging in extracurricular activities can enhance students’ understanding of real-world applications of theoretical knowledge.
6, Foster critical thinking:
- Encourage the development of analytical and evaluative skills.
- Example: Encouraging debates and discussions in classrooms can foster critical thinking among students.
7, Implications of corporate decisions:
- The consequences or effects of choices made by businesses.
- Example: Understanding the implications of corporate decisions is crucial for students pursuing careers in business management.
8, Responsible and sustainable practices:
- Ethical and enduring methods of operation.
- Example: Education on environmental issues is essential for promoting responsible and sustainable practices in various industries.
9, Multidisciplinary approach:
- An approach that involves multiple areas of study.
- Example: Solving complex societal problems often requires a multidisciplinary approach that draws from various academic fields.
10, Intensive focus:
- Concentrated and dedicated attention.
- Example: Achieving success in scientific research demands an intensive focus on data analysis and experimentation.
11, Expertise:
- High level of knowledge or skill in a particular area.
- Example: After years of practice, he developed expertise in neurosurgery, making him a renowned specialist.
12, Likelihood of success:
- Probability of achieving positive outcomes.
- Example: Acquiring a solid educational foundation increases the likelihood of success in one’s professional journey.
13, Balanced approach:
- A method that considers multiple factors and avoids extremes.
- Example: A balanced approach to education involves both theoretical learning and practical application.
14, Cultivate a well-rounded individual:
- Nurture a person with diverse skills and knowledge.
- Example: A holistic education system aims to cultivate well-rounded individuals who can adapt to various challenges.
15, Undivided attention:
- Complete and focused concentration.
- Example: Achieving excellence in any field requires undivided attention and continuous effort.
16, Holistic view:
- Comprehensive and inclusive perspective.
- Example: A holistic view of history takes into account various cultural, social, and political factors.
17, Carefully manage their time:
- Skillfully handle and allocate their time.
- Example: University students must learn to carefully manage their time to balance academic commitments and personal activities.
18, Prioritize their studies:
- Give importance to their educational pursuits.
- Example: Successful students know how to prioritize their studies while still participating in extracurricular activities.
19, Comprehensive education:
- A well-rounded and thorough educational experience.
- Example: A comprehensive education equips students with the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in various fields.
20, Enrich their intellectual growth:
- Enhances their cognitive and mental development.
- Example: Engaging in critical thinking exercises can enrich students’ intellectual growth and capacity for problem-solving.
Xem thêm:
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 18 Test 1
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 18 Test 2
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 18 Test 3
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 18 Test 4
Đừng bỏ qua những cuốn sách cực hữu ích:
Lược dịch tiếng Việt
Một số sinh viên đại học tán thành việc học thêm các môn học khác bên cạnh chuyên ngành chính của họ, cho rằng việc có kiến thức đa dạng có thể nâng cao hiểu biết về thế giới và thúc đẩy tư duy phân tích. Ví dụ, một sinh viên chuyên ngành kinh doanh học thêm môn khoa học môi trường có thể hiểu rõ hơn về tác động của quyết định doanh nghiệp đối với môi trường, từ đó thúc đẩy các phương pháp làm việc có trách nhiệm và bền vững. Cách tiếp cận đa ngành này làm phong phú hơn trải nghiệm học tập của sinh viên và trang bị cho họ cái nhìn toàn diện về các vấn đề xã hội.
Mặt khác, có những người cho rằng tập trung vào chuyên ngành của họ là quan trọng, khẳng định kiến thức và kỹ năng chuyên môn là không thể thiếu trong thị trường việc làm cạnh tranh hiện nay. Ví dụ, sinh viên ngành kỹ thuật có thể tin rằng tập trung thời gian vào việc nắm vững các khái niệm và kỹ thuật kỹ thuật phức tạp sẽ giúp họ có lợi thế trong ngành công nghiệp này. Góc nhìn này cho thấy rằng tập trung sâu vào một lĩnh vực có thể dẫn đến chuyên môn và khả năng thành công cao hơn trong một lộ trình nghề nghiệp cụ thể.
Theo quan điểm của tôi, một cách tiếp cận cân đối là thích hợp. Trong khi việc đa dạng hóa các hoạt động học tập có thể phát triển cá nhân toàn diện, tập trung không phân tán vào chuyên ngành có thể thúc đẩy hiểu biết sâu sắc và thành thạo về lĩnh vực cụ thể. Cách tiếp cận này yêu cầu sinh viên quản lý thời gian cẩn thận và ưu tiên học tập của họ, đảm bảo rằng họ có lợi từ cả sự đa dạng và sự chuyên sâu trong giáo dục của mình.
Tóm lại, câu hỏi về việc liệu có nên khám phá nhiều môn học khác bên cạnh chuyên ngành chính hay tập trung hoàn toàn vào nó là phức tạp. Một sự kết hợp của cả hai cách tiếp cận, đánh giá các lợi ích của mỗi hướng, mang lại cho sinh viên một sự giáo dục toàn diện không chỉ chuẩn bị họ cho thị trường lao động mà còn làm giàu cho sự phát triển tư duy của họ.
[/stu]Mời bạn cùng tham gia cộng đồng “Học IELTS 0đ” trên Zalo cùng IELTS Thanh Loan, nhận những video bài giảng, tài liệu, dự đoán đề thi IELTS miễn phí và cập nhật