Cam 13 Test 3 Writing Task 1
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
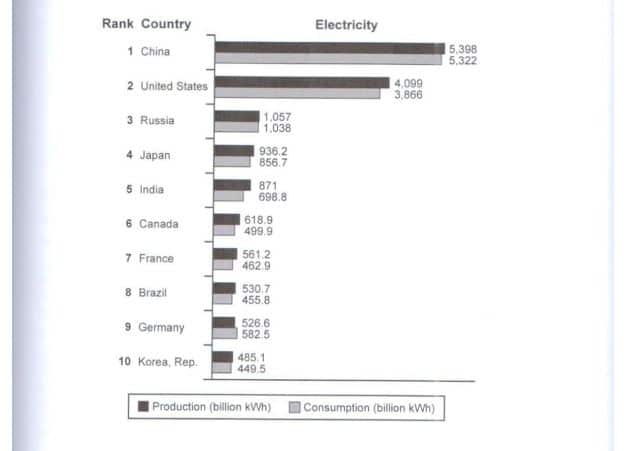
The bar chart illustrates the electricity production and consumption of ten nations in 2014.
In general, China emerged as the leading electricity producer and consumer during the period under consideration. Among the ten nations mentioned, production consistently surpassed consumption, with the exception of Germany.
In 2014, China generated nearly 5.400 billion kWh of electricity, the highest among the nations listed, while the United States produced over 4.000 billion kWh. Both countries used less electricity than they produced, with consumption figures standing at approximately 5.300 and 3.900 billion kWh, respectively.
The remaining nations exhibited significant disparities between electricity production and consumption compared to China and the United States. Notably, Russia demonstrated a minor difference between production and consumption, with just over 1.000 billion kWh. Conversely, Germany stood out by consuming more electricity than it produced, consuming 582 billion kWh compared to 526 billion kWh produced. Korea, in contrast to China, generated the least electricity and consumed the lowest amount, recording under 500 billion kWh.
Bạn đang chuẩn bị cho kì thi IELTS?
Học IELTS Online qua ZOOM, bức band thần tốc
IELTS Thanh Loan – giáo viên 10 năm kinh nghiệm – trực tiếp đứng lớp, tự tin mang đến khóa học chất lượng nhất, phương pháp giảng dạy cô đọng dễ hiểu, giáo trình tự biên soạn cho lộ trình từ cơ bản đến luyện đề chuyên sâu. Đặc biệt, học viên luôn được quan tâm sát sao nhất, hỗ trợ không giới hạn, thúc đẩy kỷ luật học tập tốt để đạt mục tiêu.

Phân tích câu hỏi
Dạng biểu đồ: Bar chart không có sự thay đổi theo thời gian. Sử dụng thì quá khứ đơn vì thời gian là năm 2014
Cấu trúc bài viết:
Introduction: Paraphrase để giới thiệu biểu đồ
- The bar chart = the chart
- shows = compares = illustrates
- the production = the generation → produce / generate / create
- the consumption = the use → consume / use
Overview:
- So sánh giữa các quốc gia → China vừa có lượng sản xuất lớn nhất và đồng thời lượng tiêu thụ cũng lớn nhất
- So sánh consumption và production → Production thường cao hơn consumption, ngoại trừ Germany
Body paragraph 1: So sánh hai nước có số liệu cao nhất (China và United State)
Body paragraph 2: So sánh các nước còn lại
Từ vựng hay
- Consistently: Adverb /kənˈsɪstəntli/
English Meaning: In a way that is steady and unchanging.
Vietnamese Meaning: Một cách kiên định và không thay đổi. - Surpass: Verb /səˈpɑːrs/
English Meaning: To exceed or go beyond in amount, degree, or excellence.
Vietnamese Meaning: Vượt qua hoặc đi xa hơn về số lượng, mức độ hoặc xuất sắc. - With the exception of /wɪð ðə ɪkˈsɛpʃən ʌv/
English Meaning: Except for; not including.
Vietnamese Meaning: Ngoại trừ; không bao gồm. - Disparity: Noun /dɪˈspærɪti/
English Meaning: A great difference or inequality, especially in age, amount, or rank.
Vietnamese Meaning: Sự khác biệt hoặc bất bình đẳng lớn, đặc biệt là về tuổi tác, số lượng hoặc cấp bậc. - Conversely: Adverb /ˈkɒnvɜːsli/
English Meaning: In an opposite or contrary manner.
Vietnamese Meaning: Một cách ngược lại hoặc trái ngược.
Lược dịch bài mẫu
Biểu đồ bảng so sánh lượng điện được sản xuất và tiêu thụ bởi mười quốc gia trong năm 2014.
Nói chung, Trung Quốc đồng thời là nhà sản xuất và tiêu dùng điện lớn nhất trong giai đoạn được mô tả. Sự tương đồng giữa mười quốc gia được đề cập là sản xuất ghi nhận con số cao hơn một chút so với tiêu dùng, ngoại trừ Đức.
Trong năm 2014, Trung Quốc đã tạo ra gần 5.400 tỷ kWh, đây là con số cao nhất trên bảng xếp hạng, so với hơn 4.000 tỷ kWh do Mỹ tạo ra. Ở cả hai quốc gia, lượng điện sử dụng thấp hơn so với sản xuất, tương ứng khoảng 5.300 và 3.900 tỷ kWh.
Các quốc gia khác cho thấy sự chênh lệch lớn trong sản xuất và tiêu thụ điện với hai quốc gia nói trên. Các đặc điểm nổi bật là Nga đã ghi nhận một sự khác biệt nhỏ giữa số lượng sản xuất và tiêu thụ năng lượng này, chỉ với hơn 1.000 tỷ kWh và Đức cho thấy sự tương phản lớn khi sử dụng nhiều điện hơn so với mức sản xuất của nó, ở mức 526 và 582 tỷ kWh. Hàn Quốc, ngược lại với Trung Quốc, đã tạo ra ít điện nhất và cũng tiêu thụ lượng thấp nhất, ghi nhận dưới 500 tỷ kWh.
[stu alias=”khoa_truy_cap_cac_bai_giai_de”]Xem thêm:
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 13 Test 1
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 13 Test 2
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 13 Test 3
- Bài mẫu Writing Task 1 & 2 Cam 13 Test 4
Đừng bỏ qua những cuốn sách cực hữu ích:
Cam 13 Test 3 Writing Task 2
Some people say History is one of the most important school subjects. Other people think that, in today’s world, subjects like Science and Technology are more important than History.
Discuss both these views and give your own opinion
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge or experience.
Bài mẫu tham khảo
In today’s educational landscape, the debate over the significance of history versus subjects like science and technology continues to garner attention. While some argue that history holds paramount importance in shaping individuals and societies, others contend that in the modern world, the emphasis should be placed on subjects that drive technological advancements and scientific discoveries. In this essay, we will explore both perspectives before offering a balanced viewpoint.
History holds significant importance in shaping our understanding of the past, present, and future. For instance, by studying historical events such as the Industrial Revolution, students can gain insights into how societal changes have shaped the modern world. Understanding the causes and consequences of historical conflicts like World War II can also provide valuable lessons in diplomacy and conflict resolution, essential for fostering peaceful coexistence in today’s globalized society.
Similarly, science and technology play pivotal roles in driving progress and addressing contemporary challenges. For example, breakthroughs in medical science, such as the development of vaccines, have significantly reduced the impact of infectious diseases and saved countless lives. Additionally, advancements in renewable energy technologies offer sustainable solutions to environmental issues, mitigating the effects of climate change and promoting a cleaner, greener future for generations to come.