The charts below show the percentage of workers in three sectors across four countries in 1980 and 2010. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
Bài mẫu
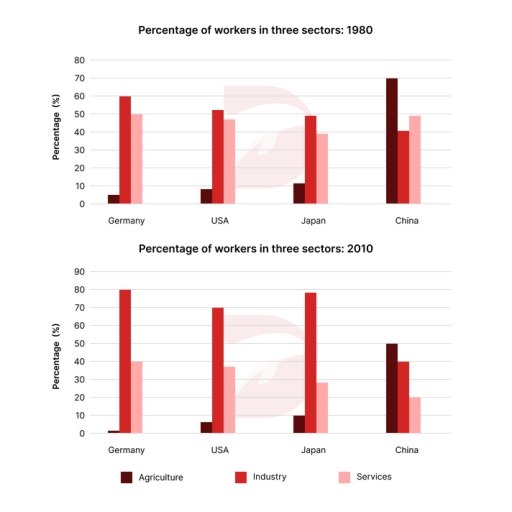
The bar charts illustrate the employment distribution across sectors in four nations between 1980 and 2010.
Overall, there was a downturn in agricultural and service employment, while industrial employment generally surged across all countries except China. In China, agriculture maintained the highest employment share in both years, while industry dominated in the other countries.
In 1980, Germany exhibited a predominant industrial workforce at 60%, with services and agriculture at 50% and 5% respectively. Similarly, the USA and India had comparable patterns, with roughly half in industry and nearly another half in services and a small minority in agriculture. In contrast, China’s workforce was primarily agricultural, at 70%, exceeding services and industry by 20% and 30% respectively.
By 2010, there was a surge in industrial employment in Germany, the US, and Japan, reaching 70% to 80%, while China’s industrial sector remained stable at 40%. China experienced a notable 30% decline in services, compared to around 10% in the other countries. Agricultural employment in China also dropped by 20%, contrasting with negligible changes in the other nations, each accounting for less than 10%.
Từ vựng tốt trong bài
- employment distribution (n): sự phân bổ việc làm
Giải thích: the allocation or spread of jobs across different sectors, regions, or demographic groups within an economy
Ví dụ: The government is implementing policies to improve employment distribution by promoting job opportunities in rural areas.
- surge (v): tăng nhanh
Giải thích: to increase suddenly and strongly
Ví dụ: The company’s profits have surged.
- dominate (v): át hẳn, trội hơn, chiếm ưu thế; có ảnh hưởng lớn, chi phối
Giải thích: to be the largest, most important, or most noticeable part of something
Ví dụ: The cathedral dominates the landscape for miles around.
- industrial workforce (n): lực lượng lao động công nghiệp
Giải thích: the group of workers employed in industries involved in manufacturing, production, or construction
Ví dụ: Automation has led to a decline in the size of the industrial workforce as machines replace manual labor in factories.
- has comparable patterns (v): có xu hướng tương đương
Giải thích: to exhibit similar trends or characteristics
Ví dụ: The two datasets had comparable patterns of growth and decline over the past decade, indicating a strong correlation between the variables.
- negligible (adj): không đáng kể
Giải thích: so small or insignificant as to be not worth considering; insignificant
Ví dụ: The impact of the new tax policy on small businesses was negligible, as the changes were minimal and had little effect on overall profitability.
Bạn đang chuẩn bị cho kì thi IELTS?
Hãy tham khảo Khóa Học IELTS Online qua ZOOM cùng cô Thanh Loan
IELTS Thanh Loan – giáo viên 10 năm kinh nghiệm – trực tiếp đứng lớp, tự tin mang đến khóa học chất lượng nhất, phương pháp giảng dạy cô đọng dễ hiểu, giáo trình tự biên soạn cho lộ trình từ cơ bản đến luyện đề chuyên sâu. Đặc biệt, học viên luôn được quan tâm sát sao nhất, hỗ trợ không giới hạn, thúc đẩy kỷ luật học tập tốt để đạt mục tiêu.

Lược dịch tiếng Việt
Biểu đồ minh họa sự phân bổ việc làm giữa các ngành ở bốn quốc gia từ năm 1980 đến năm 2010.
Nhìn chung, việc làm trong lĩnh vực nông nghiệp và dịch vụ đã suy giảm, trong khi việc làm trong công nghiệp nhìn chung tăng mạnh ở tất cả các quốc gia ngoại trừ Trung Quốc. Ở Trung Quốc, nông nghiệp duy trì tỷ lệ việc làm cao nhất trong cả hai năm, trong khi công nghiệp chiếm ưu thế ở các quốc gia khác.
Năm 1980, Đức có lực lượng lao động công nghiệp chiếm ưu thế với tỷ lệ 60%, dịch vụ và nông nghiệp lần lượt là 50% và 5%. Tương tự, Hoa Kỳ và Ấn Độ có mô hình tương tự nhau, với khoảng một nửa trong ngành công nghiệp và gần một nửa khác trong dịch vụ và một thiểu số nhỏ trong nông nghiệp. Ngược lại, lực lượng lao động của Trung Quốc chủ yếu là nông nghiệp, ở mức 70%, vượt dịch vụ và công nghiệp lần lượt là 20% và 30%.
Đến năm 2010, số việc làm trong ngành công nghiệp ở Đức, Mỹ và Nhật Bản tăng vọt, đạt 70% đến 80%, trong khi khu vực công nghiệp của Trung Quốc vẫn ổn định ở mức 40%. Trung Quốc đã trải qua sự sụt giảm đáng chú ý về dịch vụ 30%, so với khoảng 10% ở các quốc gia khác. Việc làm trong nông nghiệp ở Trung Quốc cũng giảm 20%, trái ngược với sự thay đổi không đáng kể ở các quốc gia khác, mỗi quốc gia chỉ chiếm dưới 10%.
Xem thêm: